WiFi Generations: Understanding The Evolution And Future Of Wireless Technology
Wireless internet has become an essential part of modern life, and WiFi generations play a crucial role in shaping our connectivity experience. From streaming movies to working remotely, WiFi technology has revolutionized how we interact with the digital world. As we delve into this article, you'll learn about the evolution of WiFi standards and their impact on daily life.
WiFi is not just a convenience; it is a necessity for businesses, households, and individuals around the globe. Over the years, the technology has undergone significant advancements, leading to faster speeds, better coverage, and improved reliability. Understanding the different WiFi generations will help you make informed decisions about your connectivity needs.
This article will explore the history, technical aspects, and future prospects of WiFi generations. By the end, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of how WiFi has evolved and what to expect in the coming years. Let's dive in!
Read also:Guy Martin Net Worth 2024 A Comprehensive Guide To His Financial Success
Table of Contents
- Introduction to WiFi Generations
- The History of WiFi
- WiFi Generations Explained
- Key Features of Each WiFi Generation
- WiFi Speeds Across Generations
- Applications of WiFi Generations
- Comparison of WiFi Generations
- The Future of WiFi Generations
- WiFi Standards and Certifications
- Conclusion and Recommendations
Introduction to WiFi Generations
WiFi generations refer to the various iterations of wireless networking technology that have been developed since its inception. Each generation brings improvements in speed, range, and efficiency, catering to the growing demands of internet users worldwide. The first WiFi standard, 802.11, was introduced in 1997, and since then, several updates have been released to enhance performance.
Understanding WiFi generations is essential for anyone looking to optimize their network setup. Whether you're a tech enthusiast, a business owner, or simply someone who relies on WiFi for daily activities, knowing the differences between these generations can help you choose the right equipment and plan for the future.
The History of WiFi
The journey of WiFi began in the late 1990s when the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) developed the 802.11 standard. This marked the birth of wireless networking as we know it today. Over the years, the technology has evolved significantly, with each new standard building on the strengths of its predecessors while addressing existing limitations.
Key Milestones in WiFi Development
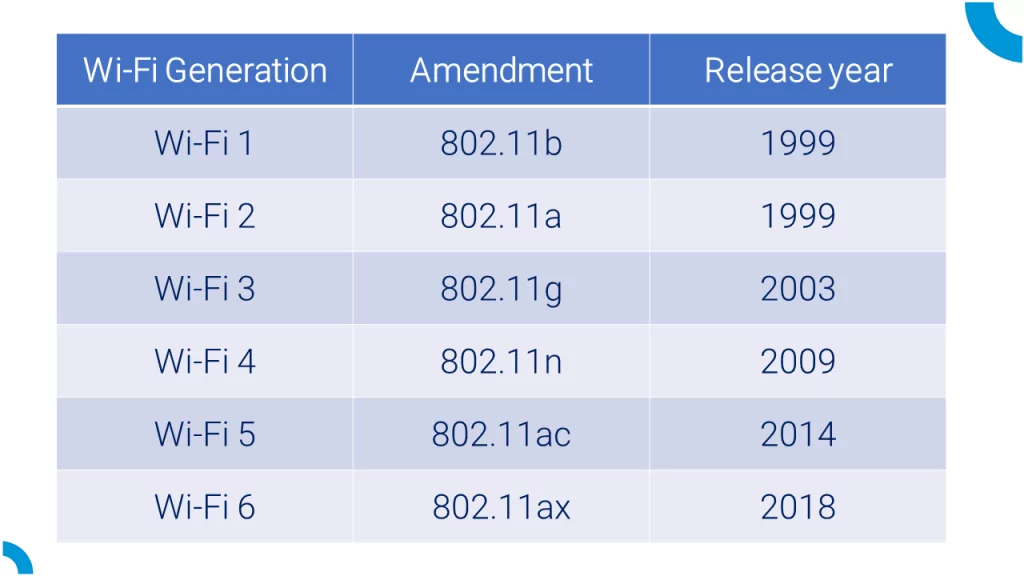
- 1997: The first 802.11 standard was released, offering speeds of up to 2 Mbps.
- 1999: 802.11b and 802.11a were introduced, increasing speeds to 11 Mbps and 54 Mbps, respectively.
- 2003: 802.11g brought improved performance in the 2.4 GHz band, offering speeds of up to 54 Mbps.
- 2009: 802.11n marked a major breakthrough with speeds exceeding 100 Mbps and support for multiple input and output (MIMO) technology.
WiFi Generations Explained
Each WiFi generation corresponds to a specific IEEE 802.11 standard. These standards define the technical specifications for wireless communication, including frequency bands, modulation techniques, and data rates. Below is a breakdown of the major WiFi generations:
WiFi 1 (802.11b)
Released in 1999, WiFi 1 operated on the 2.4 GHz band and offered speeds of up to 11 Mbps. Although outdated by today's standards, it laid the foundation for modern WiFi technology.
WiFi 2 (802.11a)
Also launched in 1999, WiFi 2 operated on the 5 GHz band and provided faster speeds of up to 54 Mbps. However, its limited range and higher cost made it less popular than WiFi 1.
Read also:Sam Heughan The Resilience Beyond The Spotlight Ndash Understanding His Brothers Battle With Cancer
Key Features of Each WiFi Generation
Each WiFi generation introduces unique features that enhance performance and usability. Here's a closer look at the key characteristics of the latest WiFi standards:
WiFi 4 (802.11n)
- Operates on both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands.
- Supports MIMO technology for improved data transfer rates.
- Maximum theoretical speed of 600 Mbps.
WiFi 5 (802.11ac)
- Limited to the 5 GHz band.
- Introduces multi-user MIMO (MU-MIMO) for better device handling.
- Maximum theoretical speed of 3.5 Gbps.
WiFi Speeds Across Generations
Speed is one of the most critical factors when evaluating WiFi generations. Over time, advancements in technology have led to dramatic improvements in data transfer rates. For instance, WiFi 6 (802.11ax) offers theoretical speeds of up to 9.6 Gbps, making it ideal for high-bandwidth applications such as 4K streaming and online gaming.
Here's a comparison of WiFi speeds across generations:
| Generation | Standard | Maximum Speed |
|---|---|---|
| WiFi 1 | 802.11b | 11 Mbps |
| WiFi 4 | 802.11n | 600 Mbps |
| WiFi 6 | 802.11ax | 9.6 Gbps |
Applications of WiFi Generations
The applications of WiFi technology are vast and varied. From smart home devices to industrial automation, WiFi generations cater to a wide range of use cases. Below are some of the most common applications:
Smart Homes
WiFi 5 and WiFi 6 are particularly well-suited for smart home environments, where multiple devices need to connect simultaneously without compromising performance.
Enterprise Networks
Businesses benefit from the enhanced capacity and reliability of newer WiFi generations, enabling seamless collaboration and communication within the workplace.
Comparison of WiFi Generations
When comparing WiFi generations, it's important to consider factors such as speed, range, and compatibility. While older generations may still suffice for basic tasks, investing in newer technology ensures better performance and future-proofing.
Here's a quick comparison:
- WiFi 4: Ideal for casual users with modest speed requirements.
- WiFi 5: Suitable for households with multiple devices and high-bandwidth needs.
- WiFi 6: Best for cutting-edge applications and heavy users.
The Future of WiFi Generations
The evolution of WiFi technology shows no signs of slowing down. Researchers are already exploring the potential of WiFi 7 (802.11be), which promises even faster speeds and greater efficiency. With advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning, future WiFi generations may offer intelligent network management and enhanced security features.
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, the demand for robust and reliable wireless connectivity will only grow. Staying informed about the latest developments in WiFi technology is crucial for anyone looking to stay ahead of the curve.
WiFi Standards and Certifications
To ensure compatibility and performance, WiFi devices must adhere to specific standards and certifications. The WiFi Alliance, a global organization, is responsible for testing and certifying products based on the latest WiFi standards. Look for the official WiFi certification logo when purchasing networking equipment to guarantee quality and reliability.
Conclusion and Recommendations
In conclusion, WiFi generations have played a pivotal role in shaping the modern digital landscape. From the early days of 802.11b to the cutting-edge capabilities of WiFi 6, each iteration has brought significant improvements to wireless connectivity. Understanding the differences between these generations will empower you to make informed decisions about your networking needs.
We encourage you to explore further by reading related articles and staying updated on the latest developments in WiFi technology. Don't forget to share your thoughts in the comments section below and consider subscribing to our newsletter for more insightful content.
Remember, the right WiFi generation can transform your connectivity experience, whether you're streaming movies, working remotely, or managing a smart home. Stay connected, stay informed, and embrace the future of wireless technology!