What Is The Difference Between Race And Ethnicity? Understanding The Key Distinctions
Understanding the difference between race and ethnicity is crucial in today's diverse world. Many people use these terms interchangeably, but they carry distinct meanings. Race refers to physical characteristics that are biologically inherited, while ethnicity is tied to cultural factors such as language, traditions, and national origin. Recognizing these differences helps foster better communication and mutual respect among individuals and communities.
As society becomes increasingly globalized, the need to comprehend the nuances of race and ethnicity grows. Misunderstandings can lead to stereotypes and discrimination, which can harm social cohesion. By exploring the definitions, historical contexts, and practical implications of race and ethnicity, we can build a more inclusive and equitable society.
This article will provide an in-depth analysis of the differences between race and ethnicity, supported by data, statistics, and credible sources. Whether you're a student, educator, or simply someone curious about the topic, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to navigate these complex concepts effectively.
Read also:Is There An After Credit Scene In Beetlejuice Unveiling The Secrets
Table of Contents
- Definition of Race
- Definition of Ethnicity
- Historical Context of Race and Ethnicity
- Biological vs. Cultural Factors
- Social Implications of Race and Ethnicity
- Common Misconceptions
- Key Differences Between Race and Ethnicity
- Statistics on Race and Ethnicity
- Impact on Society
- Conclusion
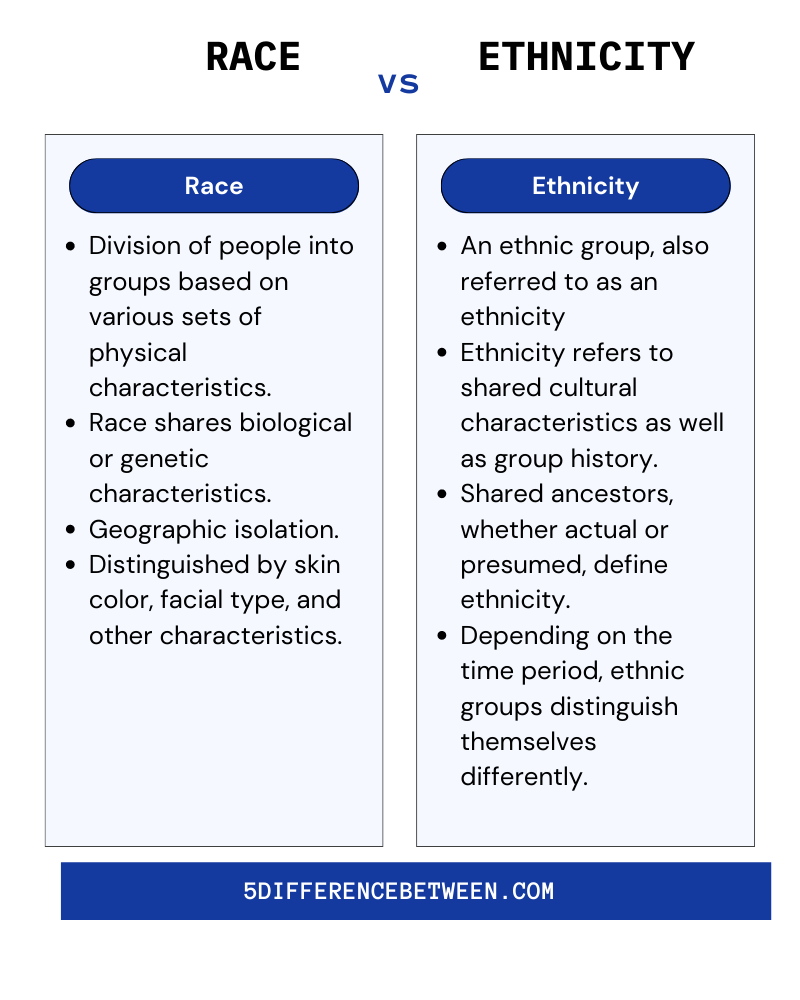
Definition of Race
Race is a classification system based on physical characteristics that are inherited biologically. These characteristics include skin color, hair texture, facial features, and genetic traits. While race is often perceived as a fixed and objective category, it is important to note that it is a social construct with no scientific basis for dividing humans into distinct groups.
How Race is Perceived
The perception of race varies across cultures and historical periods. In many societies, race has been used as a tool for categorizing people and justifying inequality. For example, during the colonial era, racial hierarchies were created to justify exploitation and oppression. Today, race continues to influence social dynamics, but its meaning is shaped by cultural and political contexts.
Examples of Racial Categories
- African American
- Caucasian
- Asian
- Indigenous
Definition of Ethnicity
Ethnicity, on the other hand, refers to the cultural identity of a group of people. It encompasses shared characteristics such as language, religion, traditions, and national origin. Unlike race, ethnicity is not based on physical traits but rather on cultural and social factors that individuals may choose to embrace or reject.
Characteristics of Ethnicity
Ethnic identity is often shaped by a combination of factors, including:
- Ancestral heritage
- Cultural practices
- Language and dialect
- Religious beliefs
Examples of Ethnic Groups
- Hispanic
- Irish
- Korean
- Maori
Historical Context of Race and Ethnicity
The concepts of race and ethnicity have evolved over time, influenced by historical events and social movements. In the 19th century, race was used as a pseudoscientific justification for slavery and colonization. Ethnicity, meanwhile, was often tied to national identity and migration patterns. Understanding this historical context is essential for addressing contemporary issues related to race and ethnicity.
Key Historical Events
- The transatlantic slave trade
- Colonialism and imperialism
- Civil rights movements
- Immigration policies
Biological vs. Cultural Factors
One of the key distinctions between race and ethnicity lies in their underlying factors. Race is rooted in biological traits, although these traits are not determinative of human behavior or capabilities. Ethnicity, by contrast, is entirely cultural and reflects the shared experiences and traditions of a group.
Read also:Mia And Grit Inspiring Stories Of Two Women Who Made An Impact
Scientific Perspectives
Modern genetics has shown that there is more genetic variation within racial groups than between them. This challenges the notion that race is a meaningful biological category. Instead, race is better understood as a social construct shaped by historical and cultural forces.
Social Implications of Race and Ethnicity
The differences between race and ethnicity have significant social implications, affecting everything from employment opportunities to access to healthcare. Racial discrimination often leads to systemic inequalities, while ethnic diversity can enrich communities and foster innovation.
Addressing Inequality
To address the social implications of race and ethnicity, it is important to promote policies that encourage inclusivity and equality. This includes:
- Implementing anti-discrimination laws
- Providing equal access to education and healthcare
- Encouraging cross-cultural dialogue
Common Misconceptions
Despite widespread awareness of the differences between race and ethnicity, many misconceptions persist. Some people believe that race is a fixed and unchangeable category, while others assume that ethnicity is synonymous with nationality. Clarifying these misunderstandings is essential for fostering greater understanding.
Myths About Race
- Race determines intelligence or abilities
- Racial categories are scientifically valid
Myths About Ethnicity
- Ethnicity is the same as nationality
- Ethnic identity is always inherited
Key Differences Between Race and Ethnicity
While race and ethnicity are often conflated, they represent distinct concepts with unique characteristics. Below are the key differences:
- Race is based on physical traits, while ethnicity is based on cultural factors.
- Race is a social construct, while ethnicity reflects personal identity.
- Racial categories are often imposed by society, while ethnic identity is chosen by individuals.
Statistics on Race and Ethnicity
Data from various studies highlight the complexity of race and ethnicity in modern society. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the population is becoming increasingly diverse, with significant growth in multiracial and multicultural communities.
Key Statistics
- As of 2020, the U.S. population identified as multiracial increased by 276% since 2010.
- Hispanic/Latino populations account for 18.7% of the U.S. population.
- Asian populations are projected to become the largest immigrant group by 2055.
Impact on Society
The differences between race and ethnicity have far-reaching implications for society, influencing everything from politics to pop culture. Recognizing and respecting these differences can lead to greater social harmony and collaboration. However, failing to address issues of race and ethnicity can perpetuate division and conflict.
Building an Inclusive Society
To build a more inclusive society, it is important to:
- Promote education and awareness about race and ethnicity.
- Encourage respectful dialogue and mutual understanding.
- Support policies that address systemic inequalities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the difference between race and ethnicity is essential for navigating today's diverse world. While race is based on physical characteristics and is a social construct, ethnicity is rooted in cultural identity and personal choice. By recognizing these distinctions, we can work towards a more inclusive and equitable society.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site that delve deeper into related topics. Together, we can foster greater understanding and respect for the rich diversity of human experience.
Data and insights in this article are drawn from reputable sources, including the U.S. Census Bureau, academic studies, and cultural analyses. For further reading, consider exploring works by scholars such as Kwame Anthony Appiah and Cornel West, who have contributed significantly to the discourse on race and ethnicity.